D. Silage - product of acid fermentation of green crops that have been compressed & stored anaerobically
1. Needs
- proper moisture (50 to 70%)
- proper stage of maturity
- proper packing
- proper drainage
- exclude air
2. Making Silage
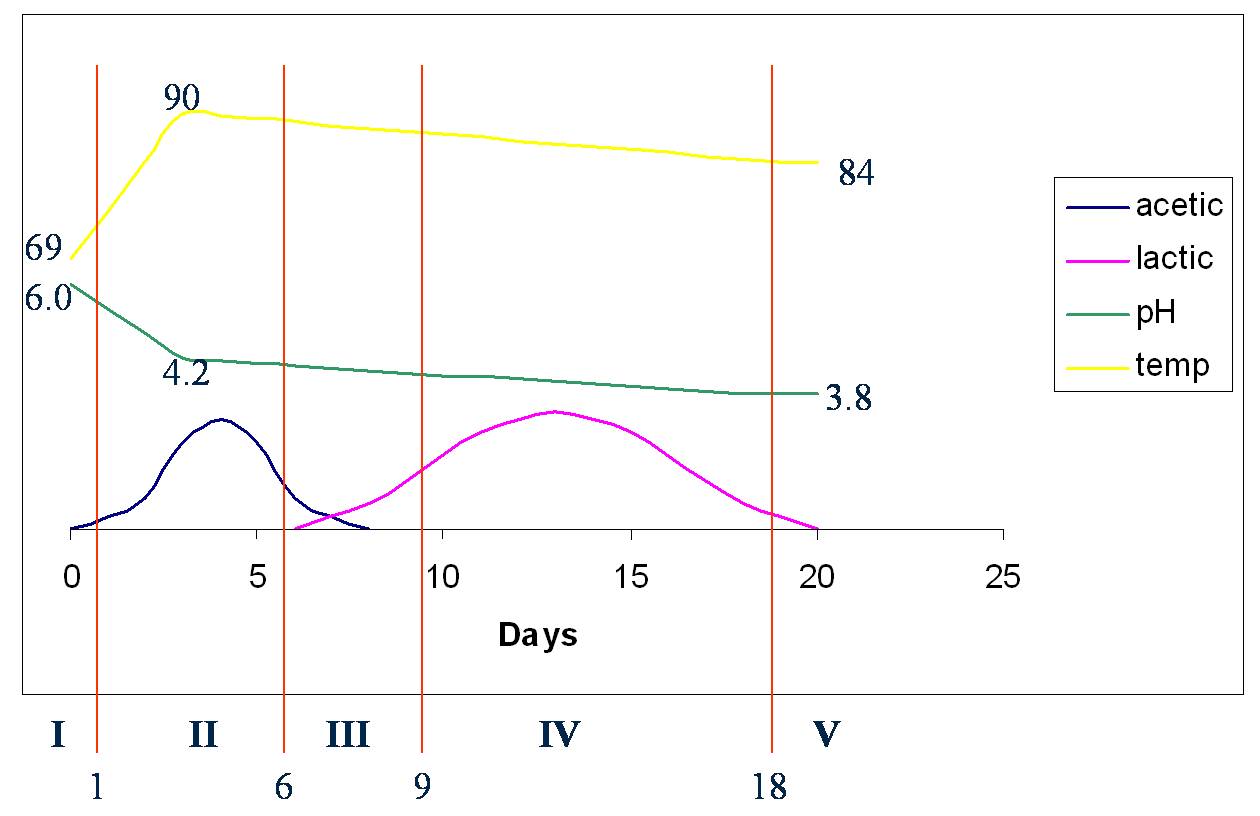
Phase 1- plant cells continue to respire; microbes use O2; CO2 & heat produced
Phase 2- acetic acid is produced (pH: 6.0 to 4.2)
Phase 3- lactic acid foramtion begins and acetic acid formation decreases
Phase 4- lactate production continues for 10 to 14 days, temperature gradually �, bacterial action ceases (pH ~ 4.0)
Phase 5- silage constant; if pH not low enough - butyric acid production! L
II. Processing Feedstuffs (WHY)
A. Grinding
1. Hammermill
2. Burrmill (more uniform grind, pass between two plates)
B. Dry Rolling
1. Compressed between two rollers (flake)
C. Pelleting
1. Made with combination of heat, moisture, & pressure
D. Heat Treatment
1. Steam Rolling (crimping; not much improvement over dry rolling) - short term exposure to steam
2. Steam Flaking (long term exposure to steam), alters starch, feed becomes more digestible (cereal smell - quite pleasant)
3. Preasure Flaking (more expensive)
4. Roasting (puffed & slightly carmalized product)
5. Extruding (heat & presure à forced through a hole makes a ribbon à breaks into flakes
6. Popping (700-800oF for 15 to 30 seconds)
7. Micronizing (exposed to microwaves, expands - but doesn�t pop)
E. High Moisture Harvesting (25 to 30% moisture)
1. No ADG effect
2. Feed efficiency is improved
F. Reconstituted High Moisture Grain
1. Add H2O to dry grain to á moisture to 25-30%
2. May improve feed efficiency but not as much as high moisture harvesting (leaching??)
G. Acid Preserved High Moisture Grain
1. Preserve with organic acids (acetic:propionic or propionic) thouroughly blended with high moisture grains. Prevents mold growth.
Balancing Rations
A) Formulate a swine diet containing 20% CP using corn and soybean meal. As-fed basis.
C) Fixed Ingredients: Formulate 1 ton of a cattle diet that contains 12.5% CP. The diet will contain 17% oats and 3% of a vitamin/mineral premix as fixed ingredients. Remainder of the diet will be corn and cottonseed meal. As-fed basis.
1) Amount of fixed ingredient and CP from each.
2000 X .17 = 340 lbs oats X .091 = 30.94 lb CP
2000 X .03 = 60 lbs v/m pmx X 0 = 0 lb CP
400 lbs 30.94 lbs CP
2) Need 250 lbs CP
- 30.94
219.06 lbs CP still needed from corn and CSM
3) X = lbs Corn
1600 - X = lbs CSM
4) .088(X) + .443(1600 - X) = 219.06
-.355X = -489.74
X = 1379.55
5) Final Diet
1379.55 lbs Corn
220.45 lbs CSM
340 lbs Oats
60 lbs Vit/Min Premix