CARBOHYDRATES
General:
Carbon containing compounds that also contain H & O in the same ratio as water (H2O) CH2O, C6H12O6Major energy source of the body CHO > fat > protein
Monomer:
basic building block. For CHO = monosaccharides; (protein = a.a.)Glucose-
major energy source for most cells. No free glucose is ingested. Enzymes must degrade CHO's to single glucose (mono) units.I. Monosaccharides:
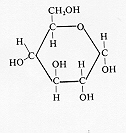
single unitA. Hexoses:
6 carbona. Glucose
b. Fructose
c. Galactose
-not free in nature = usually linked to something elsed. Mannose
B. Pentoses
a. Arabinose
b. Xylose
c. Ribose
(found in DNA & RNA)II. Disaccharides
A. Sucrose
B. Lactose
(galactose + glucose)C. Maltose
(glucose + glucose; a 1,4)D. Cellobiose
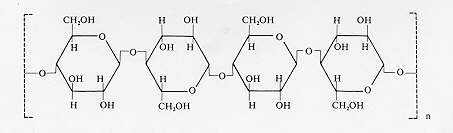
(glucose + glucose; b 1,4)III. Polysaccharides
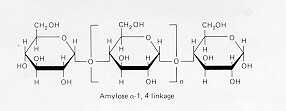
B. Amylopectin
(a 1,4 links with a 1,6 branches)C. Glycogen
(same as amylopectin, but much more branching - 2-3 X)